The Sun: The Star of Our Solar System
The Sun: The Star of Our Solar System

The sun, a massive ball of hot, glowing gas, is the center of our solar system and the primary source of energy for our planet. Without the sun, life on Earth would not be possible. In this article, we will explore the sun's structure, its importance to our planet, and some fascinating facts about our star.
Structure of the Sun
The sun is a massive celestial body, with a diameter of approximately 1.4 million kilometers (870,000 miles), which is 109 times wider than Earth, and you could fit roughly 1.3 million Earths inside it. It is composed of about 75% hydrogen and 25% helium, with trace amounts of heavier elements. The sun's structure can be divided into several layers:
1. Core: The core is the central region of the sun, where nuclear reactions take place. These reactions involve the fusion of hydrogen atoms into helium, releasing vast amounts of energy in the process.
2. Radiative Zone: Surrounding the core is the radiative zone, where energy generated by nuclear reactions is transferred through radiation.
3. Convective Zone: The convective zone is the outer layer of the sun, where energy is transferred through convection. Hot plasma rises to the surface, cools, and then sinks back down, creating a circulating motion.
4. Photosphere: The photosphere is the visible surface of the sun, the layer that we can see. It is the source of sunlight, which is emitted as a result of the sun's internal heat and energy.
5. Corona: The corona is the outer atmosphere of the sun, extending millions of kilometers into space. It is much hotter than the photosphere, with temperatures ranging from a few thousand to millions of degrees Celsius.
Importance of the Sun to Our Planet
The sun plays a vital role in supporting life on Earth. Here are some of the ways in which the sun is essential to our planet:
1. Energy Source: The sun is the primary source of energy for our planet. It provides the energy that powers the Earth's climate, weather patterns, and the water cycle.
2. Photosynthesis: The sun's energy is used by plants to undergo photosynthesis, the process by which they convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen.
3. Vitamin D Production: Exposure to sunlight triggers the production of vitamin D in our skin, which is essential for maintaining healthy bones and immune systems.
4. Climate Regulation: The sun's energy helps regulate the Earth's climate, influencing the formation of clouds, precipitation patterns, and temperature fluctuations.
Fascinating Facts About the Sun
Here are some interesting facts about the sun:
1. Age: The sun is approximately 4.6 billion years old and has already burned through about half of its hydrogen fuel.
2. Size: The sun is so massive that it makes up about 99.8% of the mass of our solar system.
3. Surface Temperature: The surface temperature of the sun is about 5,500 degrees Celsius (10,000 degrees Fahrenheit).
4. Light Travel Time: It takes about 8 minutes and 20 seconds for sunlight to travel from the sun to the Earth.
5. Solar Flares: The sun experiences massive solar flares, which can release as much energy as billions of nuclear bombs.
6. The Sun is White: While we perceive the Sun as yellow, it actually emits white light.
Here's an overview of some of the significant research done on the Sun:
Early Research (17th-19th centuries)
1. Galileo Galilei: Observed sunspots, providing evidence for the Sun's rotation.
2. Isaac Newton: Developed the laws of motion and universal gravitation, laying the foundation for understanding the Sun's behavior.
3. Joseph von Fraunhofer: Discovered the Sun's spectral lines, which are still used today to study the Sun's composition.
20th-Century Research
1. Nuclear Reactions: Hans Bethe and Carl von Weizsäcker independently proposed the proton-proton chain reaction as the source of the Sun's energy.
2. Solar Wind: Eugene Parker predicted the existence of the solar wind, a stream of charged particles emanating from the Sun.
3. Coronal Heating: Researchers like Lyman Spitzer and Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar investigated the mysterious heating of the Sun's corona.
Space-Based Research (1960s-present)
1. Skylab: Launched in 1973, Skylab was the first space station to study the Sun, providing valuable data on solar flares and coronal heating.
2. Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO): Launched in 1995, SOHO has been monitoring the Sun's activity, including sunspots, solar flares, and coronal mass ejections.
3. Hinode: Launched in 2006, Hinode has been studying the Sun's magnetic field, solar flares, and coronal heating.
Recent Research (2000s-present)
1. Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO): Launched in 2010, SDO has been monitoring the Sun's activity, including sunspots, solar flares, and coronal mass ejections.
2. Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph (IRIS): Launched in 2013, IRIS has been studying the Sun's chromosphere and transition region.
3. Parker Solar Probe: Launched in 2018, the Parker Solar Probe has been exploring the Sun's corona and solar wind.
Ongoing and Future Research
1. Daniel K. Inouye Solar Telescope (DKIST): Currently under construction, DKIST will be the world's largest solar telescope, studying the Sun's magnetic field and solar flares.
2. European Space Agency's (ESA) Solar Orbiter: Scheduled to launch in 2022, Solar Orbiter will explore the Sun's polar regions and magnetic field.
3. NASA's Sun Radio Imaging (SRI) mission: Proposed for launch in the late 2020s, SRI will study the Sun's corona and solar wind using radio imaging.
India's significant contributions
India has made significant contributions to understanding the Sun through its research initiatives. One notable example is the Aditya-L1 mission, launched on September 2, 2023, by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO). This mission aims to study the Sun's corona, chromosphere, and photosphere, providing valuable insights into solar phenomena.
Key Objectives of Aditya-L1 Mission:
- Understanding Coronal Heating and Solar Wind Acceleration
- Studying Initiation of Coronal Mass Ejection (CME), Solar Flares, and Near-Earth Space Weather
- Analyzing Coupling and Dynamics of the Solar Atmosphere
- Investigating Solar Wind Distribution and Temperature Anisotropy
The Aditya-L1 spacecraft is equipped with seven payloads, including:
- Visible Emission Line Coronagraph (VELC): Studies the solar corona and observes dynamics of Coronal Mass Ejections.
- Solar Ultra-violet Imaging Telescope (SUIT): Captures images of the Solar Photosphere and Chromosphere in near Ultraviolet (UV).
- Solar Low Energy X-ray Spectrometer (SoLEXS): Functions as a Soft X-ray spectrometer, studying X-ray flares from the Sun.
- High Energy L1 Orbiting X-ray Spectrometer (HEL1OS): Acts as a Hard X-ray spectrometer, investigating X-ray flares from the Sun.
- Aditya Solar Wind Particle Experiment (ASPEX): Studies solar wind and energetic ions.
- Plasma Analyser Package for Aditya (PAPA): Gathers data on plasma characteristics and composition in the interplanetary space.
- Advanced Tri-axial High-Resolution Digital Magnetometers (MAG): Measures the low-intensity interplanetary magnetic field in space.
These payloads enable the Aditya-L1 mission to provide unprecedented insights into the Sun's behavior, ultimately enhancing our understanding of space weather and its impact on Earth.
These are just a few examples of the significant research that has been conducted on the Sun. Ongoing and future research will continue to advance our understanding of the Sun and its impact on our solar system.
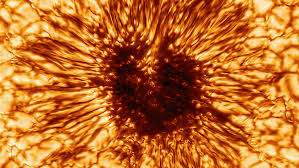
The "Sun Spot" image
In conclusion, the sun is a remarkable celestial body that plays a vital role in supporting life on Earth. Its energy is essential for our planet's climate, weather patterns, and the water cycle. As we continue to explore and learn more about the sun, we are reminded of its importance and the impact it has on our daily lives.
TALENTS INFINITE TALENTS (TIT).
“Be the change you want to see Universally,”
👉 YOUTUBE https://www.youtube.com/@TalentsInfiniteTalents
👉 EMAIL : talents.infinite.talents@gmail.com
👉 TO JOIN US / CHAT WITH US: https://chat.whatsapp.com/BwdkONnYBM2E8Yy3RSdvu9
👉 WHAT’S APP NUMBER: +91 8681095579
.png)
.jpeg)
.png)
.png)










Comments
Post a Comment